
The Importance of Data Integration in Digital Health Platforms
Learn more about the benefits of a data-driven model in healthcare.
Data is the key to the future of health businesses everywhere. The usage of big data in this industry has become a new form of competitive advantage that exceeds any other value in the market. Becoming a data-driven organisation is necessary for today’s business environment - providing better strategies, better inputs on past, present and future company growth and, ultimately, better stakeholder decision-making.
Digital has paved its way into almost every aspect of the health business. With the effects of big data usage, this showcases an excellent opportunity to process all information reliably and securely. Thus, avoiding getting lost in the vast amount of data is essential for efficient use of all the information collected through digital health tools. Therefore, one way to simplify and act on the matter is by centralising and integrating all information in one place.
Data integration is necessary for healthcare businesses who are developing digital platforms. Having homogenous and connected health data information empowers the concept of centralised healthcare and patient-centred care, which have proven to be a tremendous approach in aiding clinical decisions, improving primary and preventive care, and overall patient experience.
This article will discuss how data integration is essential for digital health platforms to improve the quality of care and reduce medical errors and costs for patients and health systems. It will also analyse the challenges data integration faces and the benefits of continuous data integration.
Data literacy in the health industry
In today's digitalised environment, healthcare organisations must shift towards a data-driven system. This journey might be complex, but it is essential for their success. In this sense, data literacy is a vital skill that will empower individuals at all levels in the organisation to collect, analyse, and use data to make informed decisions. To achieve high levels of data literacy and optimise data usage, health systems can implement a program based on four fundamental elements:
- Infrastructure
- Access
- Support
- Privacy and security
Healthcare data literacy plays an essential role in having a data-driven business model. By empowering users to understand health data and use it confidently to make clinical and business decisions, data literacy broadens their perspective to include data insight and analytics.
Prioritising data and becoming a data-driven healthcare organisation must begin at the top, with leadership driving the change, emphasising the importance of data literacy at every level and acknowledging that the process of becoming data-driven is a continuously evolving state that relies on the availability of analytical tools and talent.
Once the leadership establishes that data is the path to pursue and be invested in, the next step is assessing the organisation’s data literacy and learning needs at different levels, as showcased in the framework below.
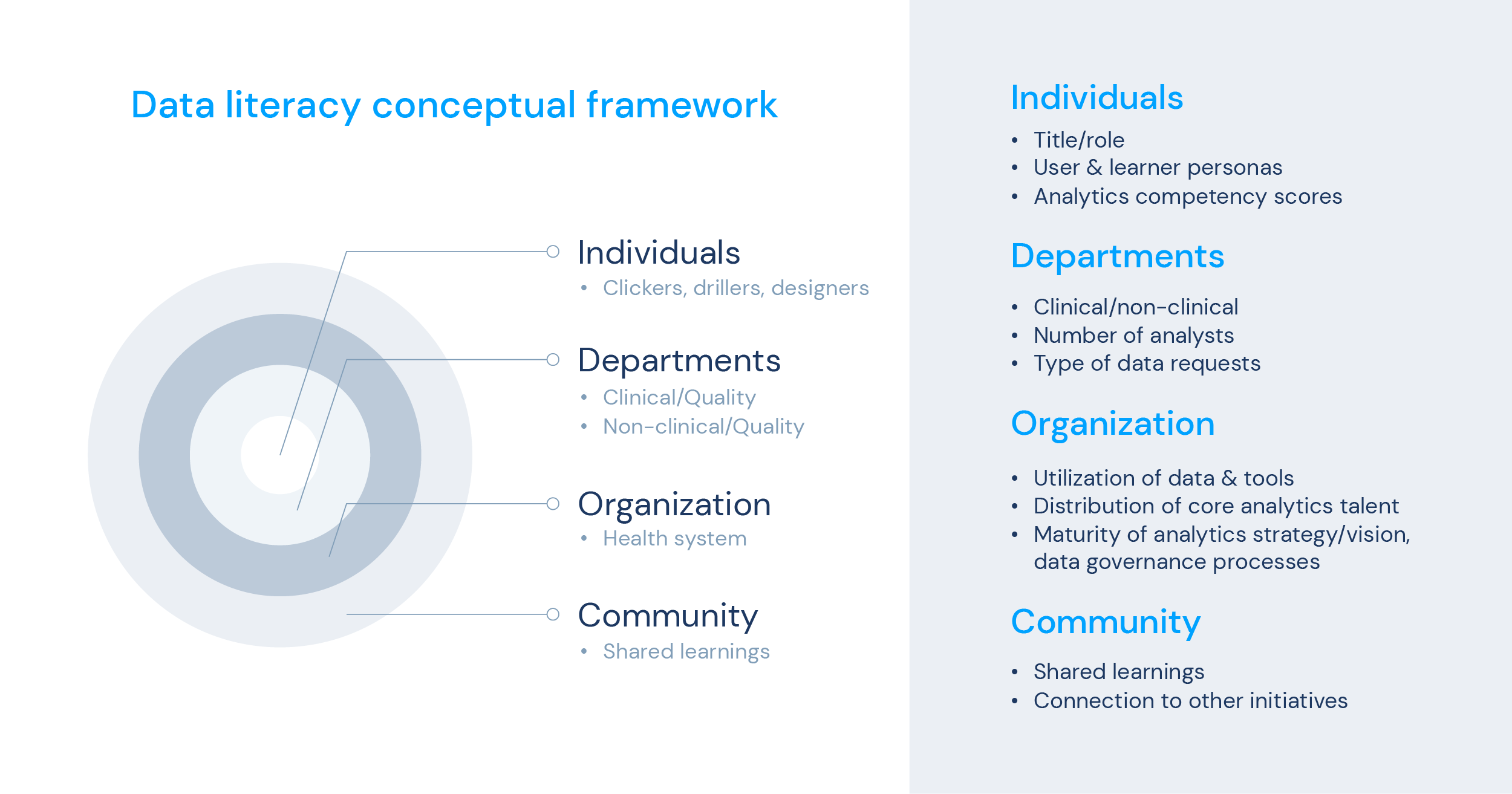
Establishing a data literacy program can be invaluable for healthcare organisations at any stage of their journey towards data-driven operations. By promoting the effective use of reliable data to generate actionable insights, such programs would help prepare team members with the skills and knowledge needed to drive sustained improvements.
When more individuals within an organisation – from all levels and departments - can adeptly collect, manage, evaluate, and rigorously apply data, they are better positioned to achieve meaningful and enduring outcomes.
Also, as previously demonstrated in article 2, data literacy accelerates effective analytics use. It improves clinical, operational, and financial outcomes, proving to be more sustainable in the long run for the business. By implementing and promoting data literacy education, members of the organisation are incentivised to use the available technology, which reduces ad-hoc requests of admin support tasks, and promotes self-service tools and outcomes more quickly. Healthcare businesses will improve employee engagement, confidence, and performance with continuous data literacy assessments and education.
The journey to a data-driven model
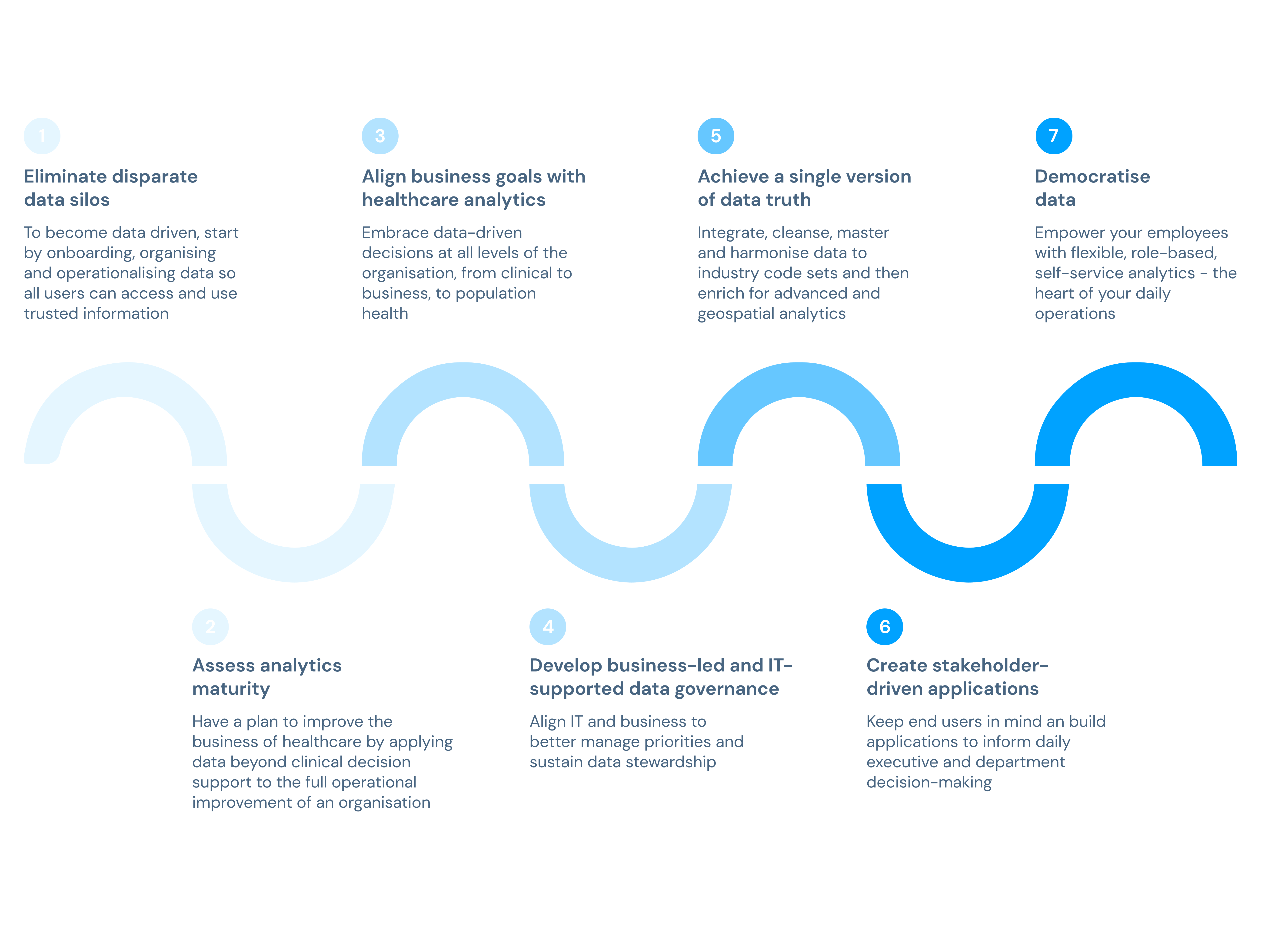
The healthcare industry needs more connected information systems and, consequently, homogeneous health data. As the healthcare industry moves toward digital health solutions and patient-centred care models, it's critical to address the challenge of insufficient data integration at the system level. This is an issue that prevents clinicians from gaining a complete understanding of a patient's condition, and it also deprives patients of the opportunity to develop a comprehensive awareness of their medical status.
Conducting a gap analysis of an organisation's data ecosystem and defining a data strategy are critical steps to embedding the importance of data into the organisation. Data analysis is critical for high-quality healthcare for several reasons:
- Improving patient outcomes: Data analysis can help healthcare providers identify patterns and trends indicating potential health risks and allowing for early intervention and better management of chronic conditions. Healthcare providers can make more informed decisions that improve patient outcomes by analysing patient data.
- Reducing costs: Analysing data can help healthcare organisations identify inefficiencies and waste areas, which is pivotal to lowering costs. By analysing the data, healthcare providers can determine the most effective treatment options, leading to better resource allocation and cost savings.
- Enhancing patient safety: Data analysis can help identify potential safety issues by detecting patterns and trends that may not be immediately apparent. By analysing patient data, healthcare providers can also identify possible drug interactions, errors in medical records, and other risks, improving patient safety.
- Identifying areas for improvement: Ultimately, it can also aid healthcare providers in identifying areas for improvement in healthcare delivery, such as gaps in patient care or high readmission rates. By identifying these areas of concern, healthcare providers can implement targeted interventions and improve the quality of care.
Overall, data analysis is crucial for building a more data-driven healthcare system. Healthcare generates vast data, from patient records and medical imaging to clinical trials and public health statistics. By applying data analysis techniques, healthcare professionals can extract actionable insights and make better-informed decisions, leading to improved patient outcomes, lower costs, and more efficient healthcare delivery.
To implement a successful data-driven healthcare system, providers and insurers can focus on developing and establishing digital health tools and frameworks that help boost data collection and analysis for a more efficient overall process.
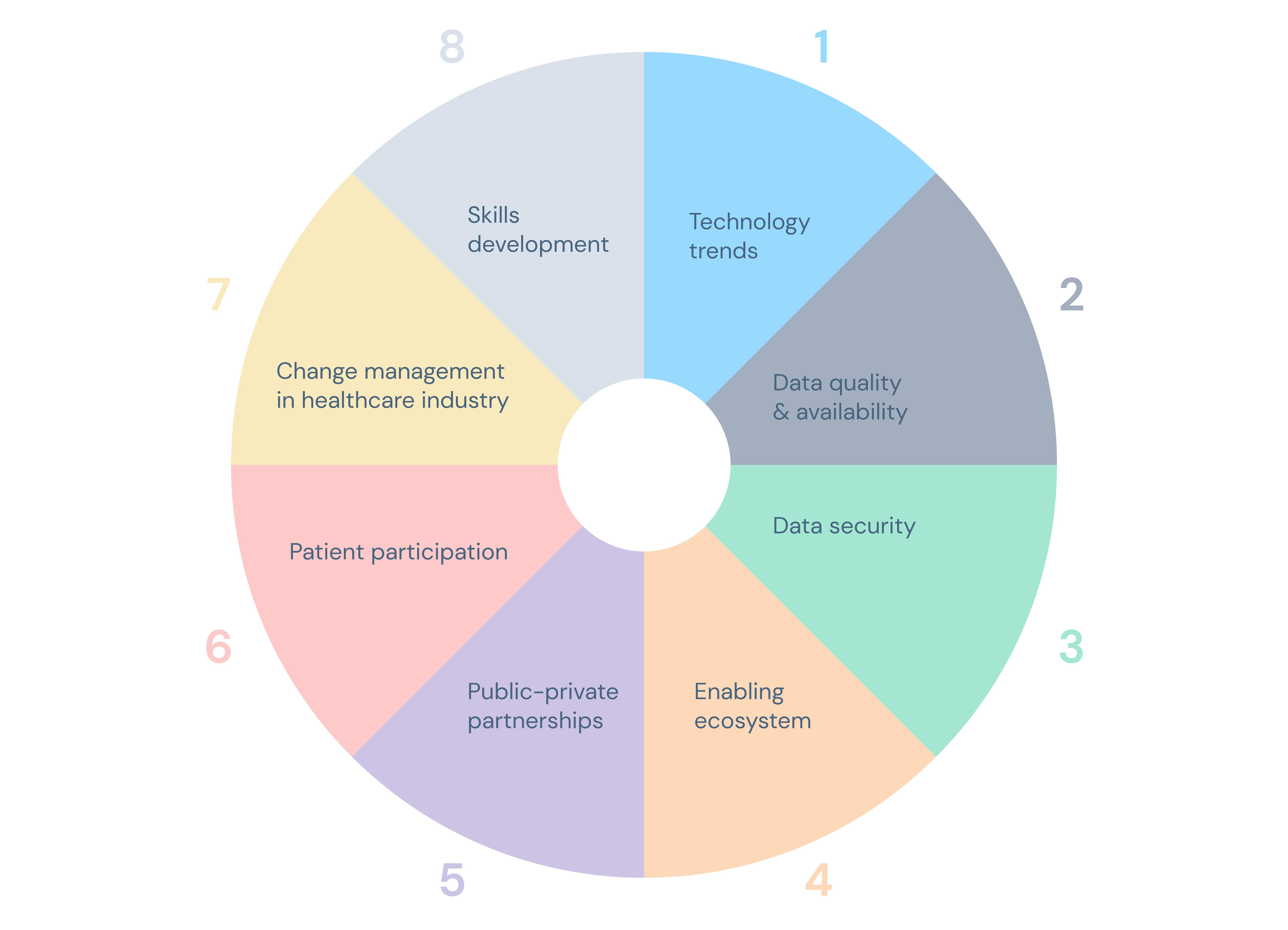
8 drivers of data-driven healthcare
There are different frameworks and models proposed for drivers of data-driven healthcare. Still, one commonly cited framework includes the following eight drivers:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): EHRs are digital records of patient's health information, including medical history, diagnoses, medications, and test results. EHRs enable data collection, sharing, and analysis across healthcare organisations.
- Wearables and sensors: Wearable devices and sensors can track vital signs, activity levels, sleep patterns, and other health-related data in real-time, providing a continuous stream of data for analysis and monitoring.
- Data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI): Data analytics and AI tools can help analyse large and complex datasets to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and generate more informed decisions. These tools can also support personalised treatment, population health management, and cost reduction.
- Precision medicine: Precision medicine aims to tailor medical treatment to individual patients' genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. It relies on genomic data, biomarkers, and other data sources to identify the most effective patient treatments.
- Patient engagement and empowerment: Patient engagement and empowerment demand the involvement of patients in their own healthcare decisions by providing them with access to their health data. This can improve patient outcomes and satisfaction and enhance the accuracy and completeness of health data.
- Telehealth and remote monitoring: Telehealth and remote monitoring technologies allow patients to access healthcare services and providers anywhere. These technologies can improve access to care, reduce costs, and increase patient engagement.
- Interoperability: Interoperability refers to the ability of different healthcare systems and applications to exchange data seamlessly. The use of EHRs, wearables, and other data sources is essential.
- Regulatory and policy changes: Regulatory and policy changes can support or hinder the adoption of data-driven healthcare. Changes in regulations and policies can influence data privacy and security, reimbursement models, and other aspects of healthcare delivery.
Health data in a patient-centred model
Health data and big data applications have proved big bets in the health industry. Following this question, reviewing how the patient-centred model utilises data and how this system can improve medical assistance and operations is essential.
The advances in digital health have created new opportunities for developing and implementing patient-centred healthcare (PCC) models in medical practices of all sizes. Also known as value-based care, PCC is a concept that heavily supports augmented telemedicine action as it focuses on illness prevention and efficiency in health outcomes rather than illness treatments.
Here, PCC goes beyond what typically separates patients and their clinical context, and it is built on the relationships formed between healthcare professionals, patients, and health organisations. The Institute of Medicine's report ‘Crossing the Quality Chasm’ identified PCC as one of six aims for high-quality healthcare, defining it as care that is "respectful of and responsive to individual patient preferences, needs, and values, and ensures that patient values guide all clinical decisions."
Patient-centred care aims to deliver individualised care through greater patient involvement and well-being, address health disparities, provide higher value for health businesses, increase employee autonomy, and provide an efficient health operations model. This requires a different system architecture, one that uses other information systems, applications or devices that actively cooperate and exchange health data, and an interoperability model.
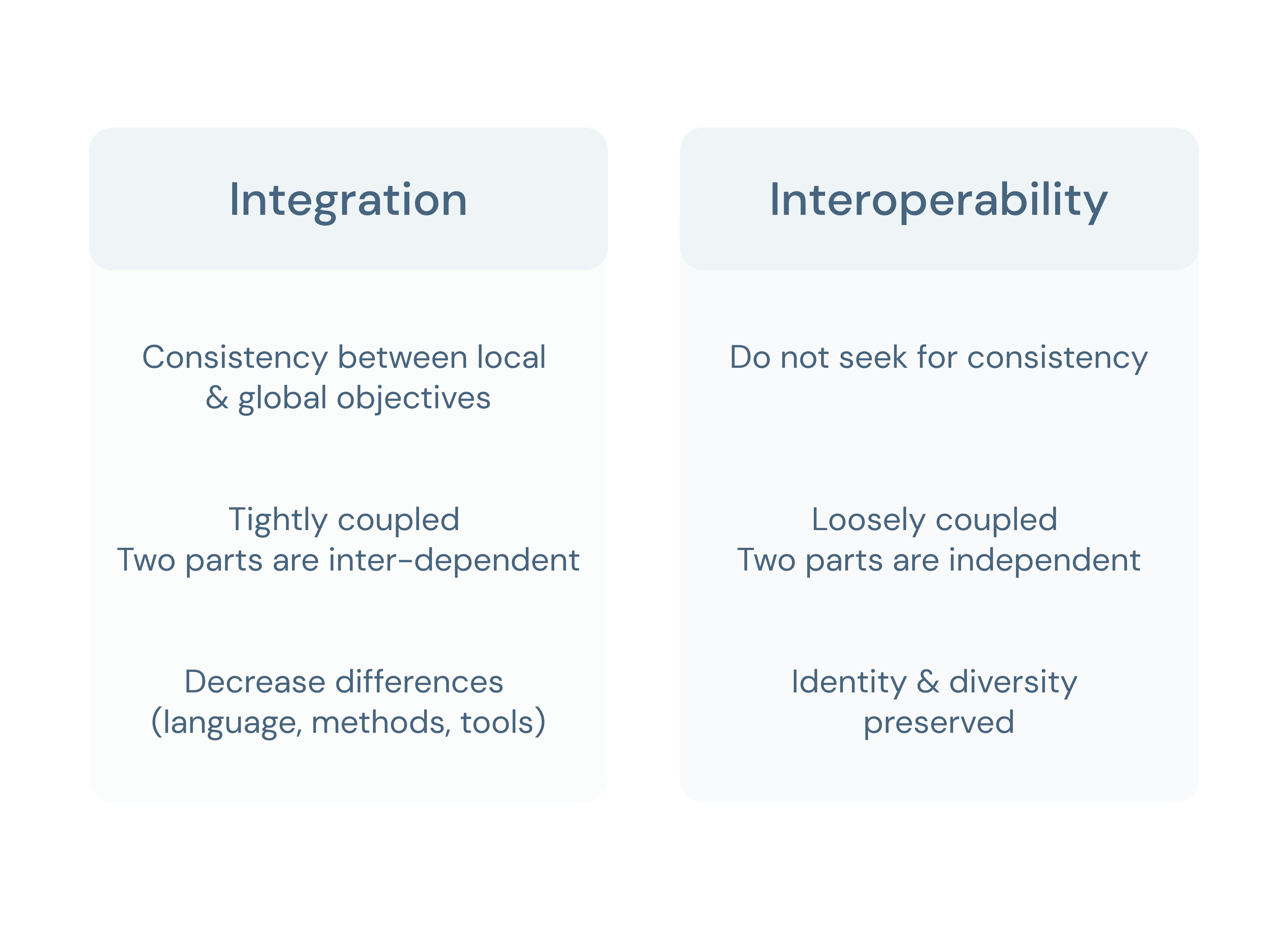
Interoperability and data integration in healthcare
Interoperability and data integration are related concepts, but they are not interchangeable. In healthcare, interoperability allows different healthcare providers to share patient data across other systems, enabling better care coordination and improved clinical decision-making.
How can data integration help clinical decision support?
It’s crucial to have a comprehensive and integrated approach to healthcare delivery that puts patients at the centre of care. In “A data integration platform for patient-centred e-healthcare and clinical decision support”, the authors present an open data integration platform designed to enable patient-centred e-healthcare and clinical decision support. This platform uses data from different sources, from EHR, clinical support systems and patient-filled data, into one system.
According to these authors, having a fully data-integrated platform is necessary for delivering high-quality healthcare and “a practical solution to a key healthcare need and a generic solution to better decision making in healthcare in the new ‘information age’”.
By integrating data from various sources, providers can gain a more comprehensive view of a patient's medical history and other relevant data, which enables more informed clinical decision-making. This enhances the quality of care and reduces the risk of medical errors.

Data integration platforms also facilitate better collaboration and communication among healthcare providers, leading to improved care coordination, reduced duplication of effort, and increased efficiency. These platforms enable healthcare organisations to standardise data across different systems, which is essential in ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Additionally, data integration platforms enable advanced analytics and machine learning techniques to identify patterns, trends, and insights that can inform clinical decision-making and healthcare strategy.
As healthcare increasingly digitises, data integration will become even more critical. To fully realise the benefits of integration in digital health, healthcare organisations must invest in the necessary infrastructure, updated technology and educated human resources, including establishing robust data governance processes, adopting interoperable systems, and ensuring data security and privacy.
Finally, data integration is a critical component of digital health that enables healthcare organisations to leverage data to improve patient outcomes, optimise care delivery, and reduce healthcare costs. By investing in data integration platforms and processes, healthcare organisations invest in enhanced quality of care, with fewer medical errors, and ultimately, improve patients' overall health and well-being.
Sources:
Health Catalyst: "Healthcare Data Literacy: A Must-Have for Becoming a Data-Driven Organization."
Infosys: "Data-driven health care."
Aidoc: "Data-driven healthcare: Changing the exchange of information."
HIMSS: 8 drivers of data-driven healthcare
HIMSS: Interoperability in Healthcare