
Personalised healthcare: revolutionising care delivery
Learn about the strategy that is reshaping the future of healthcare.
Personalised healthcare is a transformative approach that ensures that medical interventions, treatments, and preventive measures are tailored to individual patients based on their unique characteristics and needs. This emerging field harnesses the power of health data and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to deliver more precise and effective care. By shifting from a one-size-fits-all model to a patient-centric approach, personalised healthcare is reshaping the industry and offering numerous benefits for both patients and stakeholders.
What is personalised healthcare and how it is implemented
Personalised healthcare, also known as precision medicine or individualised medicine, revolves around customising healthcare decisions and interventions to the specific characteristics and needs of each patient. While traditional healthcare practices often rely on general guidelines or population-based data to determine treatments, personalised healthcare also considers individual variability, genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
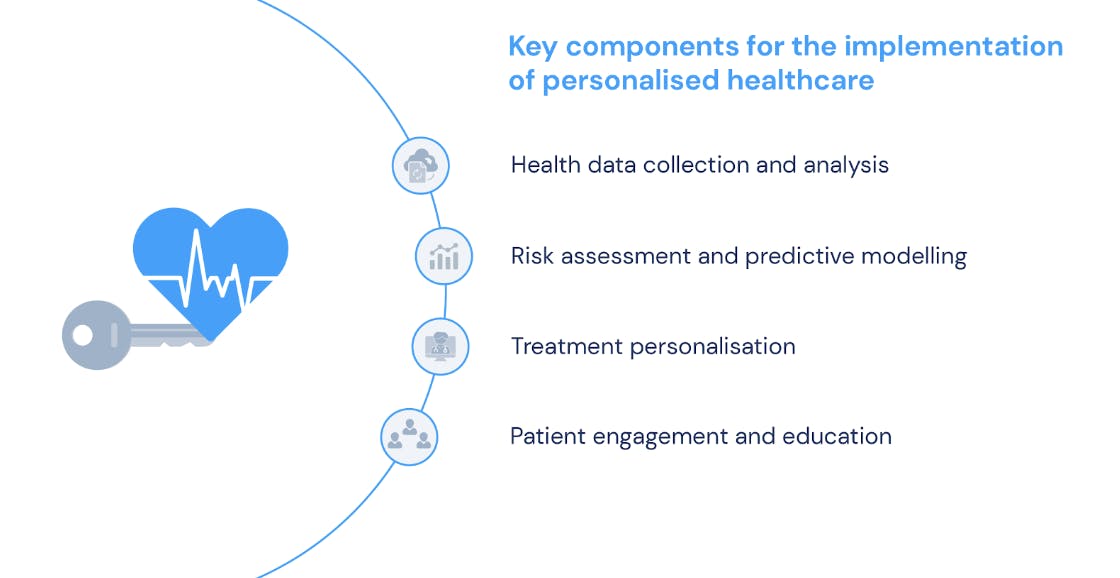
To successfully implement a personalised healthcare strategy, several key components must be taken into consideration. First of all, comprehensive accurate health data collection is essential. This includes gathering information about a patient's genetic profile, medical history, lifestyle choices, and environmental factors. In this sense, advanced technologies such as genomics, wearables, and electronic health records (EHRs) play a crucial role in the collection and analysing of this data.
Moreover, data integration and analysis are vital for extracting meaningful insights and actionable recommendations. This requires robust data management systems and analytics tools to efficiently process and interpret vast amounts of health data. In this case, AI and machine learning (ML) algorithms are often employed to identify patterns, predict disease progression, and tailor treatments accordingly.
A healthier future: the benefits of personalised healthcare
- Improved treatment efficacy
By considering individual patient characteristics, personalised healthcare enables professionals to select the most suitable treatments, medications, and dosages for each case. This targeted approach maximises treatment efficacy and minimises the risk of adverse effects.
- Enhanced disease prevention
Personalised healthcare places a strong emphasis on preventive care. By analysing genetic predispositions and lifestyle factors, healthcare providers can identify individuals at a higher risk of developing certain diseases and implement proactive measures to prevent or mitigate their onset.
- Cost savings
Targeted treatments reduce the likelihood of ineffective interventions, thereby minimising unnecessary healthcare expenditures. Additionally, personalised healthcare focuses on prevention, which enables early detection, reducing the treatment costs for advanced diseases.
- Patient empowerment
Personalised healthcare empowers patients by involving them in their own care decisions. It encourages active patient engagement and enables shared decision-making between healthcare providers and individuals. This approach enhances patient satisfaction and improves overall health outcomes.

Reshaping the healthcare industry
Personalised healthcare has far-reaching implications for various stakeholders in the healthcare industry. Here are some of the ways in which this approach impacts core stakeholders of the sector:
- Healthcare providers
Providers are adapting their practices to incorporate personalised healthcare approaches in their everyday care service delivery. They are leveraging genetic testing, data analytics, and digital health tools to make more informed diagnoses, develop tailored treatment plans, and monitor patient progress effectively.
- Pharmaceutical industry
Personalised healthcare is driving a shift towards precision medicine in the pharmaceutical industry. Companies are increasing the development of targeted therapies and medications that consider individual genetic variations, biomarkers, and disease subtypes. This new focus has the potential to revolutionise drug discovery and development processes.
- Research and innovation
This patient-centric approach is also spurring advancements in biomedical research. By analysing large-scale data sets, researchers can identify new disease associations, develop ultra-personalised treatment strategies, and discover novel biomarkers. This facilitates the development of breakthrough therapies and interventions.
- Patients
Personalised healthcare places patients at the centre of care. They are becoming more informed about their health through access to personalised data and insights. This enables them to make educated decisions about their well-being, actively participate in their treatment plans, and engage in preventive measures.

The power of data
Data is the foundation of an efficient personalised healthcare approach. By leveraging vast amounts of health data, including genetic information, medical records, lifestyle and environmental factors, healthcare providers can gain valuable insights into individual patients' health profiles. Advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms analyse this data to identify patterns and correlations to come up with predictive models.
Besides that, the integration of genomic data in personalised healthcare is particularly powerful. Genetic information can uncover inherited traits, susceptibility to diseases, and potential response to specific treatments. This knowledge allows healthcare providers to personalise treatment plans, minimise adverse reactions, and improve overall patient outcomes.
Nowadays, with the array of digital health tools, wearable devices and remote patient monitoring technologies, providers can collect real-time data on patients' health status, allowing them to perform continuous monitoring and timely interventions. These tools enable healthcare professionals to track patients' progress, identify deviations from baseline, and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
There are some case studies that evaluate the power of data in personalised healthcare:
- The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): TCGA is a ground breaking initiative that has leveraged genomic data to advance personalised cancer care. By analysing the genomic profiles of thousands of cancer patients, researchers have been able to identify specific genetic mutations associated with different types of cancer. This knowledge has led to the development of targeted therapies that can effectively address these genetic abnormalities, improving treatment outcomes and reducing side effects.
- The Framingham Heart Study: The Framingham Heart Study, a long-term epidemiological study, has utilised data to identify risk factors for cardiovascular disease. By collecting and analysing data from thousands of participants, researchers have been able to develop predictive models that estimate an individual's risk of developing heart disease. This information allows healthcare providers to implement personalised preventive measures and interventions, leading to improved cardiovascular health outcomes.
- The 100,000 Genomes Project: The 100,000 Genomes Project, conducted by Genomics England, aimed to sequence, and analyse the genomes of thousands of individuals with rare diseases and cancer. By integrating genomic data with clinical information, researchers and healthcare providers have been able to identify the genetic causes of these conditions and develop personalised treatment plans. This project has paved the way for precision medicine in the UK, leading to improved diagnostic accuracy and targeted therapies for patients.
These case studies highlight the transformative impact of data in personalised healthcare. By leveraging diverse datasets and applying advanced analytics, healthcare providers can uncover crucial insights, tailor treatments, and improve patient outcomes. The integration of genomic data, wearables, and large-scale research initiatives is revolutionising care delivery and shaping the future of personalised healthcare.
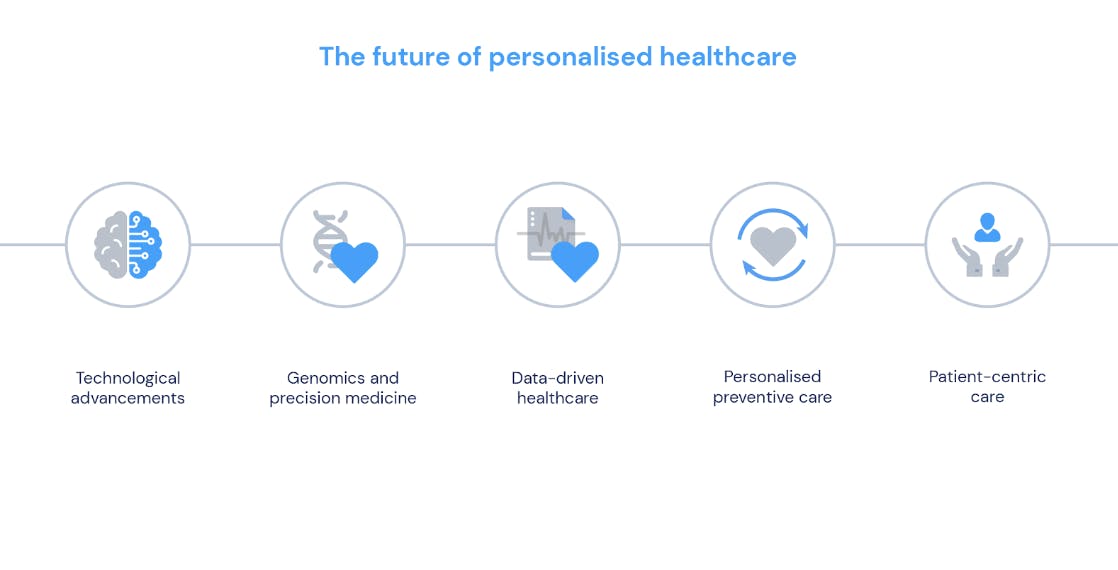
The future of personalised healthcare
Advances in personalised healthcare have the potential to revolutionise the future of care delivery. As technologies continue to evolve and become more accessible, the integration of data-driven approaches will become a standard practice.
One of the key areas of future development is the expansion of precision prevention strategies. By leveraging data and analytics, healthcare providers can identify individuals at high risk of developing certain diseases and intervene early with targeted preventive measures. This shift towards proactive healthcare has the potential to significantly reduce the burden of chronic diseases and improve population health outcomes.
Furthermore, personalised healthcare will enable the improvement of clinical trials and drug development processes. By identifying specific patient subgroups that are more likely to respond to a particular treatment, researchers can design more efficient and targeted clinical trials. This approach increases the likelihood of successful outcomes and expedites the introduction of innovative therapies into clinical practice.
Personalised healthcare represents a paradigm shift in the way healthcare is delivered. By leveraging the power of data and AI/ML algorithms, healthcare providers can tailor treatments, interventions, and preventive measures to the specific needs of individual patients. This patient-centric approach improves treatment efficacy, increases disease prevention, reduces costs, and empowers patients to actively participate in their own care.
As personalised healthcare continues to reshape the healthcare industry, stakeholders are bound to invest in data infrastructure, analytics capabilities, and regulatory frameworks to ensure the ethical and secure use of patient data. By believing in the power of health data and personalised healthcare for better outcomes, knok’s data-driven platform offers several integrated solutions that allow healthcare providers and professionals to have better insights about individual patients and target groups.
We leverage our solutions, such as our telemedicine module and our patient journey engine, with the collection of relevant health data in every step, allowing healthcare professionals to always have access to an updated EHR, exams and information shared by the patient. Furthermore, we use our own AI solution RAAGA to analyse the data collected in the most efficient way possible, delivering valuable insights that allow for a more patient-centric approach in healthcare.
References
- Severde, J. (2013). Personalised Medicine: A Critique on the Future of Health Care. School of Public Health -The University of Sydney
- NHS 75 (nd) What is personalised care?
- European Comission (nd) Personalised medicine.
- McMullen, M. (2020) What is Personalized Healthcare? Fitbid.
- Nardini, C., Osmani, V., Cormio, P. G., Frosini, A., Turrini, M., Lionis, C., & D’Errico, G. (2021). The evolution of personalized healthcare and the pivotal role of European regions in its implementation. Personalized medicine, 18(3), 283-294.
- National Cancer Institute. (2021). The Cancer Genome Atlas. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.gov/about-nci/organization/ccg/research/structural-genomics/tcga
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2021). The Framingham Heart Study. Retrieved from https://www.framinghamheartstudy.org/
- Genomics England. (2021). 100,000 Genomes Project. Retrieved from https://www.genomicsengland.co.uk/about-genomics-england/the-100000-genomes-project/